CystitisCall the inflammation of the bladder.In most cases, this inflammation is caused by bacterial infection and is a type of urinary tract infection (IMVP).The infection of the bladder can be very painful and exhausting, and can also cause more serious problems if it enters the kidneys ascending.
In rare cases, cystitis can be a reaction to certain drugs, radiotherapy or other stimuli: spraying for female hygiene, spermicidal gels or long -term use of the urinary catheter.Cystitis can also be a complication of another disease.
As a rule, bacterial cystitis requires the prescription of antibiotics.The treatment of other types of cystitis depends on their cause.
Symptoms and signs of cystitis
Symptoms of cystitis include:
Imperative (sudden and very strong) want to urinate
Misconception
Burn during urination
Frequently urgent urine
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Muddy urine and / or urine with a clear unpleasant odor
Discomfort in the basin region
Pressure pressure in the lower abdomen
Subfule body temperature (from 37 to 38 degrees)
In young children, the sudden appearance of daily enuresis (urinary incontinence) can also be a sign of urinary tract infection (IMVP).
When to see a doctor
Seek medical help immediately if you have symptoms characteristic of kidney infection, in particular:
Back pain or side
Fever and chills
Nausea and vomiting
Frequent and painful urilation, lasts more than a few hours
Blood in the urine.
It is particularly important to consult a doctor if it is not the first episode of cystitis.
If you have just finished the treatment and the symptoms have already returned, consult a doctor immediately.
If your child has daytime, call your pediatrician
Causes and risk of cystitis
The human urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, bladder and urethra (uretra).
The main function of the urinary system is to eliminate the slag from the body.The kidneys filter blood, releasing primary and then secondary urine;Secondary urine flows through the ureters in the bladder and accumulates there for several hours, after which the bladder is filled, the person feels the desire to urinate and empty the bladder through the urethra.
Bacterial cystitis
Urinal infections generally occur when bacteria from the outside penetrate the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply.Most often, cystitis is caused by e bacteria.Coli.
Bacterial cystitis can occur in women as a complication of sexual intercourse, in particular this occurs after the first sexual intercourse in the life of a woman.But even sexually inactive girls and women are sensitive to lower urinary tract infections, because women of the genitals are often obeminated bacteria that cause cystitis.
Non -infectious cystitis
Nebakterialnym Cistitam includes:
Interstitial cystitis.The causes of this chronic bladder inflammation, also called painful bladder syndrome, are not yet clear.Most often in women.This disease can be difficult to identify and heal.
Drug cystitis.Certain drugs, chemotherapeutic drugs can cause cystitis, while they accumulate in the bladder and irritate its wall.
Radiation cystitis.Radiation therapy of the pelvic area can cause inflammatory changes in the fabrics of the bladder.
Cystitis of a foreign body.The prolonged use of the urinary catheter can increase the risk of bacterial infections and tissue lesions;These two factors can cause cystitis.
Chemical cystitis.Some people may have increased sensitivity to chemicals contained in the jacuzzi, female hygiene spraying, spermicidal gels and other substances.Local chemical irritation, or allergic inflammation - causes typical symptoms of cystitis.
Cystitis caused by other factors.Sometimes cystitis can occur as a complication of other diseases, such as diabetes, kidney stones, enlarged prostate or spinal cord lesions.
Risk factors
Some people are more likely to develop recurrent urinary tract infections than others.First of all, the risk factor is female soil - a short urethra makes women more vulnerable before this disease.
Among women, those who: who:
Sexually active.Sex can lead to Protalkivaniyu bacteria in the urethra.
Use contraceptive means.Women who use diaphragms and other spermicid gel membranes are more likely to suffer from cystitis.
Pregnancy.Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of cystitis.
Located at La Ménopause.Modified hormones in women in menopause are often the IMVP Proviconyut.
Other risk factors for cystitis in men and women include:
Urine obstacle.It can be caused by a stone in the bladder or an extended prostate (in men).
Changes in the immune system.They occur in diseases such as diabetes, HIV infection and cancer chemotherapy.The removal of the immune system increases the risk of bacterial and, in some cases, viral cystitis.
Long -term use of the urinary catheter.The elderly and people with diseases may need to use the urinary catheter in the long term.This often leads to increased vulnerability before bacterial infections, as well as direct damage to the fabrics of the bladder.
In men without any predisposing factor - cystitis is rare.
Cystitis complications
With rapid and appropriate treatment, cystitis rarely leads to complications.However, with premature treatment, cystitis can cause more serious diseases.
Cystitis complications include, first of all, pyelonephritis (infectious renal inflammation).An inflamed bladder infection can fall into the ascending kidneys, which, in turn, can cause pyelonephritis and even irreversible damage to the renal tissue (nephrosclerosis).
The first children and the elderly have the highest risk of kidney damage due to the bladder infections, because the symptoms of the IMVP are often neglected or are mistaken by doctors with the symptoms of other diseases.
Preparation for a visit to a doctor
If you, or your child, have symptoms characteristic of cystitis, you should make an appointment with a doctor.First of all, you must be examined by a pediatrician, a therapist or a general practitioner, then, if he deems it necessary, you will be directed to a urologist or a nephrologist.In anticipation of the reception time, you can make a list that will reduce and optimize the communication time with the doctor:
Note your symptoms, including those that do not seem to you related to cystitis
Make a list of all drugs, vitamins or food additives you accept
Note questions you would like to ask your doctor
For example, you can ask a doctor:
What probably caused my illness?
What additional exams should I go?
What factors, in your opinion, contributed to the development of cystitis?
What type of processing approach do you recommend?
If this course does not provide relief, which treatment do you advise me afterwards?
What side effects can be expected from the course prescribed treatment?
What is the risk that this problem is repeated?
What can I do to reduce the risk of relapse?
Do I need a consultation of a close specialist, urologist or nephrologist?
Do not hesitate to ask questions that appear to you during a conversation with a doctor.
Your doctor will probably ask you a number of questions, for example:
When did you notice these symptoms for the first time?
Have you been treated for urinary tract infections earlier?
How much do you feel strong?
How often do you get wet?
After urination, how much does it last?
Do you have lower back pain?
Did you have a high temperature?
Have you noticed the release of the vagina or the blood in the urine?
Are you sexually active?
Do you use contraception creams?Which?
Aren't you pregnant?
Do you take medication, biological supplements or vitamins?Do you have any chronic diseases?
Have you ever used a urinary catheter?
Cystitis diagnosis
In addition to questioning your symptoms and your physics exam, your doctor may recommend certain tests and tests, such as:
General analysis of urineThe test is used as Skriningovy and as diagnostic.In this analysis, the IMVP can be discussed in an increase in leukocytes, red blood cells and nitrites.
Urine analysis for sterility.If the bladder is suspected of infection, the doctor may prescribe the analysis of urine for sterility, which will show the type of bacteria in the urine and their number.
General blood testThis analysis shows non -specific inflammatory changes in white blood cells and can indirectly indicate the presence and severity of the urinary tract (IMVP).
Cystoscopy.During this study, the doctor introduces a cystoscope - a thin hose with backlight and video camera, through the urethra in the bladder, and examines it from the inside to study structural anomalies and signs of inflammation.
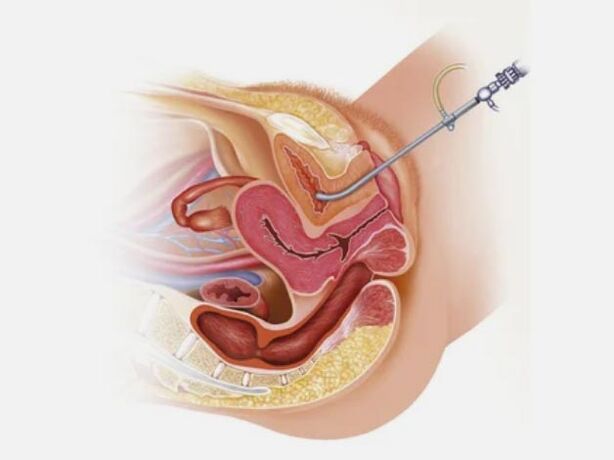
When using a cystoscope, the doctor can also take a small fabric sample (biopsy) from a suspicious location for laboratory analysis.However, cystoscopy is not shown to all patients with cystitis, but only for patients with recurring or nebakterical cystitis.
Visualisiruyushchie methods.These research methods are also necessary by all patients, but only for those who cannot find the cause of the IMVP relapse by other means.For example, radiography for the abdomen, or ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space, can identify the structural anomalies of the bladder, the ureters and the kidneys.In some cases, a contrast is carried out before the radiography, the ascendant (cystography) or the descendants (intravenous urography).
Cystitis treatment
Cystitis caused by bacterial infection is generally treated with antibiotics.The treatment of non -infectious cystitis depends on its cause.
Bacterial cystitis treatment
First -line antibiotics are active drugs against intestinal stick, or bacteria found in urine during sowing.
Primary infection.Symptoms generally improve significantly during the first days of treatment, but the doctor may insist on the therapy continues from three to seven days, depending on the severity of your infection.
Repeated infection.If you have a relapse of IMVP, the doctor may recommend a longer antibiotic treatment or directs you to a doctor specializing in the treatment of urinary tract infections (urologist or nephrologist) to identify the cause of the relapse.For some women with recurring bacterial cistitami, a single dose of antibiotic after each sex can be useful.
Nosocomial infections.Nosocomial bladder infections can be extremely difficult to treat, because the bacteria that cause them are often resistant to the main antibiotics used for the therapy of parascolary infections of the bladder.Therefore, the doctor can prescribe several antibiotics at the same time.
Treatment of interstitial cystitis
The reason for the development of interstitial cystitis remains uncertain, so there is no universal treatment plan adapted to all patients at the same time.The doctor can try the following treatment methods:
Preparations used orally or administered directly in the bladder.
Local procedures that relieve symptoms, such as stretching bladder, filling it with water or gas.
The excitation of the nerve with light electrical impulses (physiotization) to relieve pain in the pelvic area and, in some cases, reduce the frequency of the urination
Treatment of other forms of non -infectious cystitis
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause which causes non -infectious cystitis: jacuzzi, spermicidal cream, etc.
Treatment of cystitis, which develops as a complication of chemotherapy or radiotherapy, focuses on removing pain (generally using pain relievers) and washing to reduce contact with irritants in the bladder.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Cystitis can be very painful, but there are simple domestic methods to considerably facilitate this discomfort:
Use the heating cushion.Place the heating cushion in the bottom of the abdomen, this will greatly relieve pain and heaviness in the basin.
Do not allow dehydration.Drink a lot of liquids.Avoid coffee, alcohol, non -alcoholic drinks containing caffeine, citrus juices;As well as spicy foods - until the symptoms of cystitis are calomic.These substances can irritate the bladder and worsen the frequency and intensity of the urination.
Take a sedentary bath.Soup in the crotch in hot water for 15 to 20 minutes, it will significantly relieve pain and discomfort.
With recurring IMVP, discuss your optimal personal therapy and symptomatic treatment with your doctor.
Cystitis prevention
Cranberry juice or tablets containing a pro-aantocyanidin are often recommended to reduce the risk of recurring infections of the bladder of certain women.Nevertheless, recent studies show that these methods are not as effective as as previously thought.
You can always try to take cranberry juice daily, but don't forget that it cannot be combined with warfarin, because this combination can cause bleeding.
The following simple rules can be useful for prevention of cystitis:
Drink a lot of liquids, especially water.This is particularly important if you get chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Hot more often.If you feel the desire to urinate, do not pay a visit to the toilet.
After defecation, wipe the crotch on the back.This prevents bacteria in the anal region in the vagina and the urethra.
Take a shower, not a bath.If you are subject to IMVP relapses, if you refuse the bath, and you take a shower, because the standing water in the bath can help penetrate the infection into the urethra.
Gently wash the skin around the vagina and the anus.Do it daily, but do not use irritating soaps and do not make energetic efforts.On delicate skin around these areas, irritation occurs easily.
Enough the bladder as soon as possible after intercourse.Drink a full glass of water to go to the toilet soon.
Avoid the use of deodorants and aerosols, as well as other female cosmetics in the genital area.These substances can irritate the urethra and the bladder.




























